Content

For deferred revenue, the cash received is usually reported with an unearned revenue account. Unearned revenue is a liability created to record the goods or services owed to customers. When the goods or services are actually delivered at a later time, the revenue is recognized and the liability account can be removed.

If you don’t have a bookkeeper yet, check out Bench—we’ll pair you with a dedicated bookkeeping team, and give you access to simple software to track your finances. The Ascent is a Motley Fool service that rates and reviews essential products for your everyday money matters. We’re firm believers in the Golden Rule, which is why editorial opinions are ours alone and have not been previously reviewed, approved, or endorsed by included advertisers. Editorial content from The Ascent is separate from The Motley Fool editorial content and is created by a different analyst team.
Best Accounting Software for Small Businesses
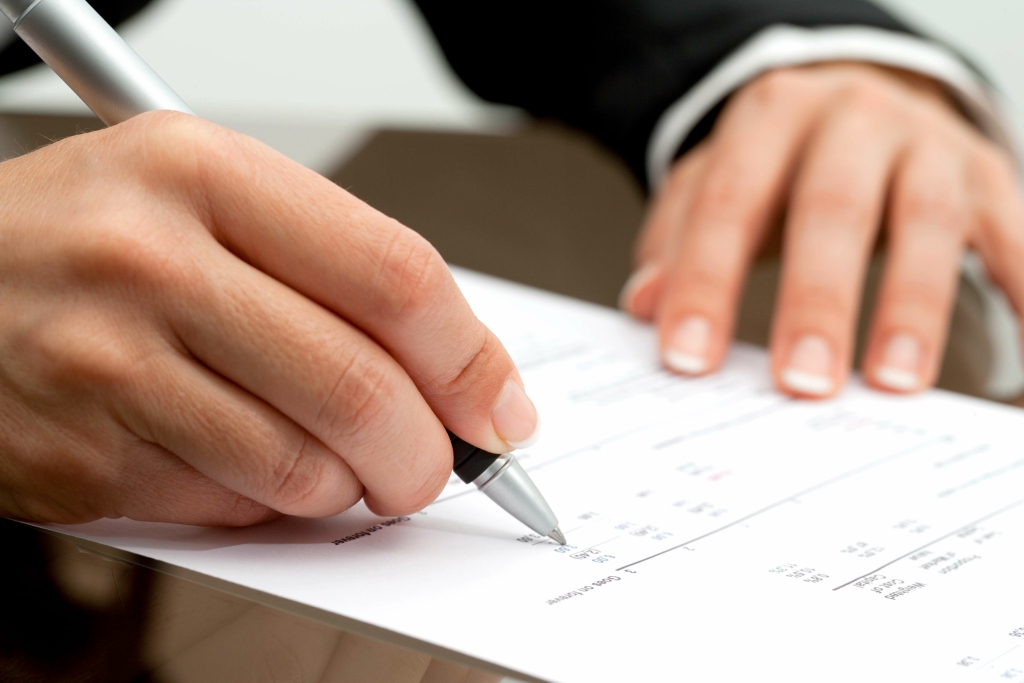
You must calculate the amounts for the https://www.bookstime.com/ and designate which account will be debited and which will be credited. Once you have completed the adjusting entries in all the appropriate accounts, you must enter them into your company’s general ledger. This category of adjusting entries is also known as unearned income, deferred revenue, or deferred income. Essentially, it refers to money you’ve been prepaid by a client before you’ve done the work or provided services. In the accrual system, this unearned income is seen as a liability and should be credited. Booking adjusting journal entries requires a thorough understanding of financial accounting.
- By definition, depreciation is the allocation of the cost of a depreciable asset over the course of its useful life.
- The matching principle says that revenue is recognized when earned and expenses when they occur (not when they’re paid).
- Adjusting entries are made for accrual of income, accrual of expenses, deferrals (income method or liability method), prepayments (asset method or expense method), depreciation, and allowances.
- Once you have completed the adjusting entries in all the appropriate accounts, you must enter them into your company’s general ledger.
- So if the ending inventory is say INR 100, and the closing balance is INR 1000, you will record INR 100 on the left side of the T-account (Dr) and the remaining INR 900 will be recorded on the right side (Cr).
- Another situation requiring an adjusting journal entry arises when an amount has already been recorded in the company’s accounting records, but the amount is for more than the current accounting period.
A common example of a prepaid expense is a company buying and paying for office supplies. An adjusting journal entry includes credits and debits of various liabilities and assets. Following the matching principle, each adjusting entry should include an equal credit and debit amount.
Examples for Adjusting Entries
Hence the income statement for December should report just one month of insurance cost of $400 ($2,400 divided by 6 months) in the account Insurance Expense. The balance sheet dated December 31 should report the cost of five months of the insurance coverage that has not yet been used up. An adjusting journal entry involves an income statement account (revenue or expense) along with a balance sheet account (asset or liability). It typically relates to the balance sheet accounts for accumulated depreciation, allowance for doubtful accounts, accrued expenses, accrued income, prepaid expenses, deferred revenue, and unearned revenue. When doing your accounting journal entries, you are tracking how money moves in your business.
How often your company books adjusting journal entries depends on your business needs. Once a month, quarterly, twice a year, or once a year may be appropriate intervals. If you intend to use accrual accounting, you absolutely must book these entries before you generate financial statements or lenders or investors. Since adjusting entries examples so frequently involve accruals and deferrals, it is customary to set up these entries as reversing entries. This means that the computer system automatically creates an exactly opposite journal entry at the beginning of the next accounting period.
Commenti recenti